How does prostatitis develop?
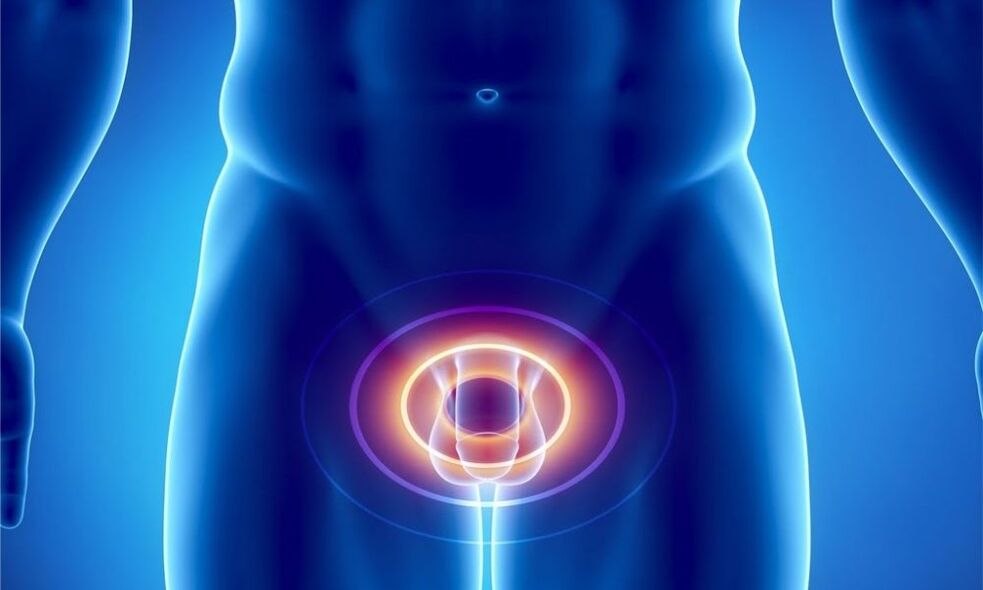
| Function | Essence |
|---|---|
| secretary | Produces a secretion that is part of the sperm. It dilutes the sperm, sets the desired pH level, and increases sperm motility. |
| engine | The muscle fibers of the gland form the urethral sphincter, which helps to suppress urine. |
| obstacle | Contains zinc peptide complex, lysozyme, cellular immune factors, and spermine to prevent the development of infection in an ascending manner. |
Influencing factors
- Pelvic circulation disorders. This can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle, excess weight, and pelvic injuries. A special risk group is drivers who are frequently in a seated position and subject their perineum to vibration and pressure. Reduced pelvic blood circulation can lead to prostate congestion and hypoxia, which can also lead to infection.
- low temperature,
- hormonal imbalance,
- urination problems,
- Irregular sexual activity - too "violent" sexual life, abstinence, interruption of sexual intercourse,
- chronic constipation,
- rectal inflammation,
- Reduced immunity makes the body vulnerable to infectious agents.
Types and symptoms of disease
- Acute bacterial prostatitis.
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis.
- CPPS – Chronic pelvic pain syndrome or chronic nonbacterial prostatitis.
- Asymptomatic prostatitis.
- catarrhalAccompanied by frequent urination and painful urination. Pain radiates to the sacrum and perineum,
- follicle.The intensity of the pain increases. It also occurs during bowel movements. Urinating becomes difficult - urine comes out in a trickle or drop. The high temperature is as high as 38°,
- Parenchyma.It is characterized by acute urinary retention and bowel problems. Severe pain in the perineum, lower back, and above the pubic bone. The body temperature rises to 38-40°. The body is poisoned, symptoms are general weakness, nausea and increased heart rate.

- pain.Interestingly, the prostate itself does not contain pain receptors. Pain occurs when the inflammatory process seizes the nerve fibers in the small pelvis, of which there are considerable numbers. It has different properties. It can be subtle or sharp and intense, disturbing even at night, subside only to return. It is located on the sacrum, scrotum, lower back, and perineum.
- Difficulty urinating.The urge to urinate becomes more frequent. It becomes sluggish and there is a feeling of a heavy, incompletely emptied bladder. The process may then improve due to compensatory increases in bladder muscle, but quickly resume. Discharge from the urethra occurs during defecation.
- Sexual disorders– Increased or decreased nocturnal erections, vague orgasms, pain during ejaculation and its acceleration. Sexual dysfunction worsens and eventually leads to impotence. There is a concept of psychogenic powerlessness when a person convinces himself that, in his situation, invasion of the intimate sphere is unavoidable. They are actually growing. As sexual dysfunction progresses, a man's mood will also change: he will become irritable and depressed.
- pain when urinating,
- Weak urine stream or dribbling,
- The feeling that the bladder is not completely empty.
How to recognize disease
- Examination by a urologist.The doctor must perform a rectal examination of the prostate. Use your fingers to push it through the rectum. It is recommended to have a bowel movement before the examination. Through manipulation, the shape and size of the glands and their consistency can be determined. This procedure helps determine the presence of tumors and inflammation in the prostate. Digital exams collect prostate secretions.
- Urinalysis.Two parts are examined: the urine collected at the beginning of urination and the urine collected at the end of the urination process. 1 copy represents the condition of the urethra and 2 copies represents the condition of the kidneys and bladder. A higher than normal number of white blood cells in the urine (15 per field) indicates inflammation.
- After collecting urine, perform prostate massage to obtain prostate secretions.If the urine is too little and is not released from the urethra but remains on the urethra wall, collect the urine after massage. It is as informative as the prostate secretions themselves. White blood cells (which should not exceed 10) are also measured here, in addition to lecithin granules and amyloid bodies. If the first gland secretion analysis does not show any abnormalities, this does not mean that there is no process. Prostatic fluid may be too thick and clog the ductal lumen of the affected gland. Healthy gland cells then produce secretions. Therefore, it is necessary to pass such an analysis multiple times. Cultures of urine and prostate secretions are also performed to identify the causative agent of the disease and determine susceptibility to antibiotics.
- General blood analysis.
- Analyze for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Kidney, bladder ultrasound, TRUS,It allows you to thoroughly assess the condition of your prostate,
- Uroflowmetry.It is used to assess the rate and timing of urine excretion. It is carried out through special equipment consisting of sensors and containers. All the patient needs to do is urinate into it in the usual way.
- Blood PSA- Prostate-specific antigen. It is an indicator of the presence of tumor formation - adenoma or cancer - in the prostate,
- Prostate biopsy.This test is done if cancer is suspected.
Treatment of acute and chronic prostatitis
- Drugs that normalize the microcirculation of organs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- It is important to maintain the body's immune function, as it can decrease under the influence of a course of antibiotics. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed immunostimulants.
- For sexual dysfunction, antidepressants and sedatives may be prescribed.
- Prostate Massage.
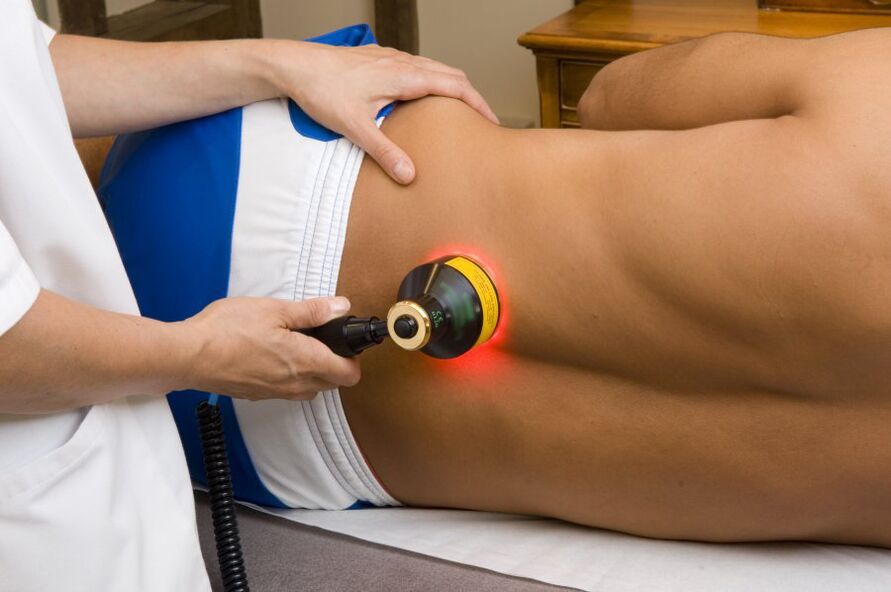
- physiotherapy:
- laser,
- ultrasound,
- rectal electrophoresis,
- Transrectal microwave hyperthermia.
- physiotherapy.
Prostate Massage: Purpose and Techniques
- acute inflammation of the prostate,
- adenocarcinoma or adenoma,
- hemorrhoid,
- Stones, cystic structures in the prostate organ.
Prostatitis and traditional medicine
- Grind 500 grams of raw, peeled pumpkin seeds through a meat grinder and mix with 200 grams of honey. The resulting material is formed into pellets. Take 2 times a day before meals, chew slowly and dissolve thoroughly. Pumpkin seeds contain high amounts of zinc, which is essential for men's health.
- Blueberries have anti-inflammatory properties. By eating 200 grams of this berry every day, you will support your male health,
- Parsley first became famous as a cooking spice. But in addition, it contains many useful substances, including those required by the male body. Take 1 tablespoon of parsley juice. Take it 3 times a day, 30 minutes before meals. This will help relieve inflammation and improve your sex life,
- Chop the green peel and thorns of the chestnuts and pour boiling water over them. used as tea
- Grind 300 grams of onions into a paste, add 100 grams of honey and 600 ml of dry wine. Store in a cool place for 1 week, stirring occasionally. tension. Use 2 tbsp. Take it 3 times a day before meals. Effective in treating chronic prostatitis.
- Squat down to just below your knees. The optimal number of times is 100 times. Do this 3 times a week. If you can't do this amount of reps at once, perform the squat in a variety of ways, resting in between.
- Scissors. Sit on the floor with your hands on the floor behind you. Stretch your legs out in front of you, lifting them off the floor. Cross them over each other. These movements are similar to the work of scissors.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees and bring them to your chest. Hug them with your arms. Stay in this position for up to 20 minutes.
- Regular walking is also a great way to relieve traffic congestion.
prostatitis in adolescents

- Premature sexual activity and sexual illiteracy.Unprotected intercourse can lead to rampant sexually transmitted infections, leading to bacterial inflammation of the prostate,
- low temperature– A contributing factor in the development of prostatitis. Temperature imbalance reduces immunity and makes the body susceptible to infection,
- fashion– Wearing clothes and underwear that are too tight can disrupt blood circulation in the pelvis and cause stagnation in the area,
- sedentary lifestyle– Computer work for modern young people has replaced sports, walking and other active pastimes,
- excessive sexual activityactually depleting the glands. Its function is reduced, secretions are released in smaller quantities and of poorer quality, making it more susceptible to infection.
Precaution
- first,Rethink your daily routine. If your job requires you to sit for long periods of time, be sure to incorporate five minutes of physical activity into your daily routine. Stretch and move around. This is necessary to make the blood "run" faster through the blood vessels. At the same time, avoid excessive physical activity to avoid physical exhaustion.
- Stop smoking. Tobacco smoke spasms blood vessels and impairs circulation, reducing the supply of oxygen to the prostate. Limit your intake of alcoholic beverages.
- Avoid hypothermia and nervousness.
- Pickled dishes are worth eating as well as spices and pickles as well as hot sauces.
- Attention should be paid to the regularity of sexual activities and the adequacy of sexual intercourse.